Ayurvedic Management of Diabetic Foot
A diabetic foot may be defined as a syndrome in which neuropathy, angiopathy and infection will lead to tissue breakdown resulting in morbidity and possible amputations.
“Every 30 minutes a limb is lost due to a landmine, every 30 seconds a limb is lost due to diabetes.”
Pathology of Diabetic Foot
The high blood sugar levels may eventually damage the nerves especially in the feet. When the nerves are damaged the patient does not feel pain and will not know that if he/she has an injury. High blood sugar levels may also damage blood vessels, resulting in poor blood supply to the area. Less blood supply means less nutrients & oxygen for the tissue cells. So, the ulcer becomes more infected and infection grows rapidly and gangrene develops. Now diabetic foot may convert in to diabetic gangrene.
Investigations Required
• ESR
• CBC count
• Platelet count
• Blood culture
• Arteriogram for blockage in blood vessels
• X-ray may be done for vascular calcification or bony erosion
Ayurvedic Management of Diabetic Foot
In Sushruta Samhita, diabetic foot is correlated with ‘madhumeha vrana’. During its description, Sushruta stated that the management of these vranas is difficult i.e. Kashtsadhaya. According to Sushruta, meda and rakta along with other dosha and dushya lead to formation of premehapidika which later is converted to non-healing wound and also further specified that wounds of lower limb are difficult to heal.
Diabetics need to know
• Daily foot inspection for redness, crack in skin or sores.
• Daily foot care. Dry completely between toes and use lotion to keep skin moist.
• Regular visit to the physician.
• Foot care education.
• Wearing proper shoes at all time. Do not go barefoot.
• Early treatment of any trouble areas.
• People with diabetes should have a foot examination every year.
• Checking for sensation (feeling) in the foot.
• Looking at the foot for changes in shape and size
• Checking blood flow and circulation.
• Looking for discoloration.
Tips for Care of Diabetic Foot
• Maintaining a persistent normal blood sugar level.
• Do aggressive measures to bring blood sugar back to normal.
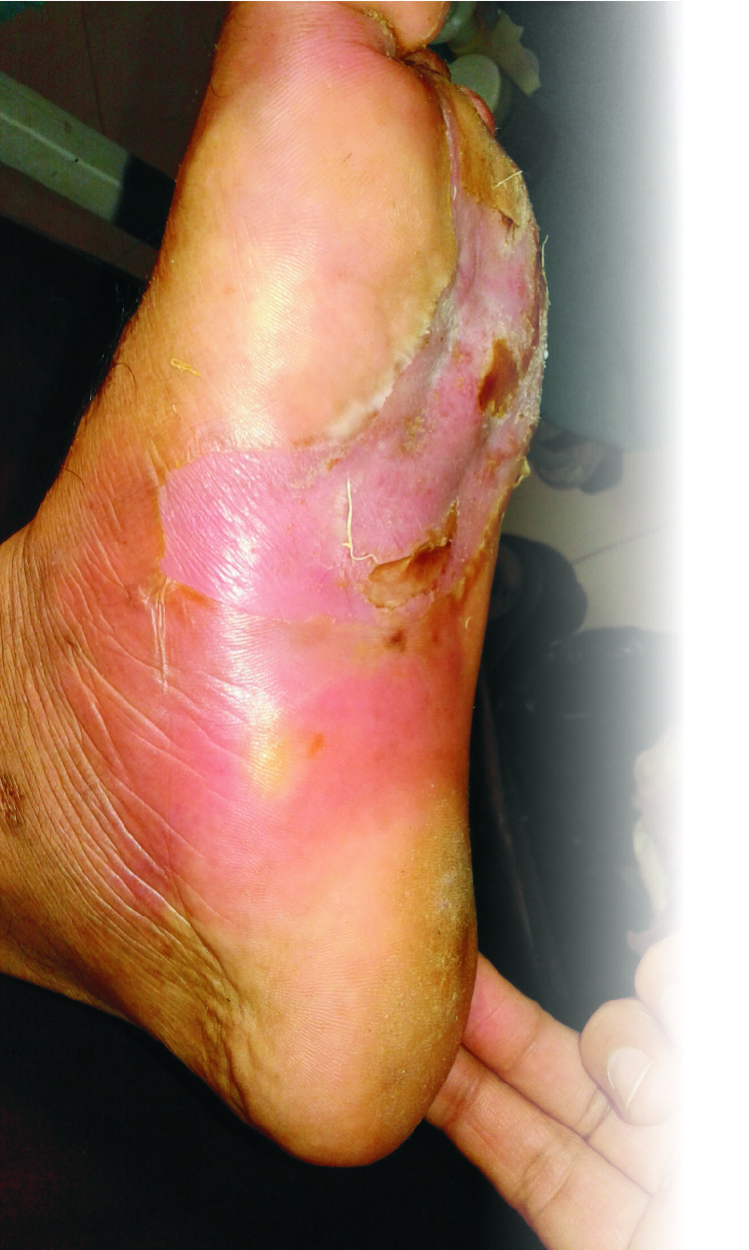
• Regular cleaning and debridement of fibrous tissue and slough.






 Dec 2024
Dec 2024
 May 2024
May 2024
 September 2022
September 2022
 April 2022
April 2022
 October 2020
October 2020
 Jan 2020
Jan 2020
 June 2019
June 2019
 January-February 2019
January-February 2019
 Augest-September
Augest-September
 April 2018
April 2018
 November 2017
November 2017
 June 2017
June 2017
 November 2016
November 2016
 September 2015
September 2015
 March 2015
March 2015
 July 2014
July 2014
 January 2014
January 2014
 July2013
July2013
 March 2013
March 2013
 May 2012
May 2012
 May 2011
May 2011
 Sep 2010
Sep 2010
 Jun 2010
Jun 2010
 Feb 2010
Feb 2010
 December 2009
December 2009
 August 2009
August 2009
 June 2009
June 2009
 Feb 2009
Feb 2009
 December 2008
December 2008
 October 2008
October 2008
 March 2008
March 2008
 July 2008
July 2008
 May 2008
May 2008